Tomato Blood Meal vs. Bone Meal: How to Tell the Difference
Can you name one key distinction between a blood meal and a bone meal? Ingredients are one of the most frequently cited distinctions between them. Due to their similarity in name alone, many are uncertain as to which is more efficient.
Blood meal and bone meal are both useful as soil supplements that add nutrients to the soil, and they can be used simultaneously. In any case, knowing the differences between blood meal and bone meal for tomatoes is important if you’re trying to decide which one to use on your tomato plants.
In addition to the changes in ingredients, we will also address the many other variables, including variances in working efficiency, best usability, efficacy, and pricing.
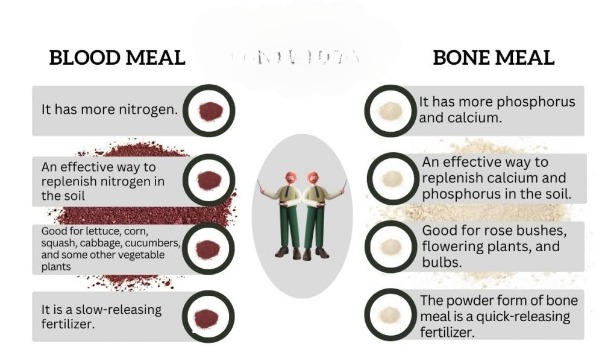
Table of Contents
Blood Meal Vs. Bone Meal For Tomatoes
| Major Differences | Blood Meal | Bone Meal |
| Ingredient Differences | It has more nitrogen. | It has more phosphorus and calcium. |
| Working Efficiency | An effective way to replenish nitrogen in the soil | An effective way to replenish calcium and phosphorus in the soil |
| Best Usability | Good for lettuce, corn, squash, cabbage, cucumbers, and some other vegetable plants | Good for rose bushes, flowering plants, and bulbs |
| Efficacy | It is a slow-releasing fertilizer. | The powder form of bone meal is a quick-releasing fertilizer. |
| Price | Costly | Cheaper |
We’ll get into the specifics of how bone meal fertilizer is different from blood meal fertilizer now.
Differences Between Blood Meal and Bone Meal Ingredients
Animal blood is dried and ground into a powder called “blood meal,” which increases the soil’s nitrogen content. With more nitrogen but less calcium and phosphorus, it can be used as a substitute for bone meal. Tomatoes need a lot of nitrogen, which is why blood meal is so important for growing them. Adding blood meal to your young tomato plants’ soil will help them produce more trusses and healthier leaves.
Bone meal, on the other hand, refers to pulverized animal bones that enrich the soil with phosphate and calcium. In addition to containing some iron, zinc, magnesium, and other micronutrients, bone meal is a great plant food. Tomato plants can benefit from this fertilizer later in the season.
Especially for cordon tomatoes, applying bone meal fertilizer to the soil when trusses begin to form has the potential to stimulate even greater flowering. However, if you want to give your tomato plant a boost of potassium, a blend of fish, blood, and bone is your best bet.
Tomatoes planted in the ground outside might benefit from this mixture again in the spring when blooms appear. Keep in mind that neither blood nor bone meals contain any potassium.
When Comparing The Working Efficiency Of The Blood Meal And The Bone Meal
Blood meal, a byproduct of the slaughterhouse, is an excellent technique to restore nitrogen levels in soil. To a greater extent than any other nutrient, nitrogen is subject to seasonal changes in soil. Your tomato plants will likely perish if you don’t give them enough nitrogen.
Tomatoes, on the other hand, can’t handle too much nitrogen, therefore it’s important to check the soil before adding any fertilizer.
Blood meal can be used to remedy low levels of nitrogen in the soil, which can be determined by doing a soil test. If you plan on replanting in the same garden bed each year, blood meal will be useful because plants have a tendency to deplete the soil. It’s also helpful to know how much water should be added to one part blood meal.
The pH of your soil will drop as a result of adding blood meal. It maintains plants’ ability to bloom and produce fruit and encourages healthy, verdant growth. Furthermore, the pungent odor of blood meal fertilizer can discourage ground squirrels, deer, or moles from digging in your garden.
If your soil tests show that it’s low in phosphate and calcium, amending it with bone meal will help your plants thrive. Keep in mind that bone meal will be somewhat useless if the soil has a pH of seven or higher, thus pH monitoring is crucial. The pH balance needs to be restored before proceeding.
In addition, high-nitrogen soil fertilizers like rotting manure can be countered by using bone meal. Plants’ root systems can be bolstered by using bone feeds. It also aids in root growth, promotes cell division, and keeps plants from becoming stunted.
Bone meal added to the soil can stimulate new growth and blooming in plants. Improved soil structure is another another benefit of using bone meal, which works by boosting the population of helpful soil bacteria.
Blood meal, a byproduct of the slaughterhouse, is an excellent technique to restore nitrogen levels in soil. To a greater extent than any other nutrient, nitrogen is subject to seasonal changes in soil. Your tomato plants will likely perish if you don’t give them enough nitrogen.
Tomatoes, on the other hand, can’t handle too much nitrogen, therefore it’s important to check the soil before adding any fertilizer.
Blood meal can be used to remedy low levels of nitrogen in the soil, which can be determined by doing a soil test. If you plan on replanting in the same garden bed each year, blood meal will be useful because plants have a tendency to deplete the soil. It’s also helpful to know how much water should be added to one part blood meal.
The pH of your soil will drop as a result of adding blood meal. It maintains plants’ ability to bloom and produce fruit and encourages healthy, verdant growth. Furthermore, the pungent odor of blood meal fertilizer can discourage ground squirrels, deer, or moles from digging in your garden.
If your soil tests show that it’s low in phosphate and calcium, amending it with bone meal will help your plants thrive. Keep in mind that bone meal will be somewhat useless if the soil has a pH of seven or higher, thus pH monitoring is crucial. The pH balance needs to be restored before proceeding.
In addition, high-nitrogen soil fertilizers like rotting manure can be countered by using bone meal. Plants’ root systems can be bolstered by using bone feeds. It also aids in root growth, promotes cell division, and keeps plants from becoming stunted.
Bone meal added to the soil can stimulate new growth and blooming in plants. Improved soil structure is another another benefit of using bone meal, which works by boosting the population of helpful soil bacteria.
Best Comparability Analysis Of These Two Soil Modifications
Plants including tomatoes, lettuce, corn, squash, cabbage, and cucumbers are all high nitrogen feeders. Fertilizers containing blood meal are beneficial to these plants, then. Some other vegetable plants, especially those that require a lot of nitrogen, benefit from the blood meal as well. Vegetables such as asparagus, melons, broccoli, eggplant, okra, peppers, and pumpkins are all in this category.
There aren’t a ton of plants that can benefit from bone meal. Rose bushes, floral plants, and bulbs all benefit from bone meal.
Differential Efficacy Of Blood Meal And Bone Meal Additives
Since blood meal dissolves in water, it can be used as a nutrient-rich plant food. In the garden, it quickly corrects nitrogen deficiencies. For 6-8 weeks after a single application, blood meal is an excellent plant food.
As a slow-release soil amendment, blood meal is of little use to a plant that requires immediate nitrogen. If you want your soil to be able to gently absorb the nutrients and be ready for the next growing season, apply blood meal to your garden bed before winter.
Bone meal can be bought in either granular or powdered form. Bone meal in granular form is a slow-release fertilizer that functions similarly to blood meal. Applying it to the soil’s surface and allowing it to slowly release nutrients in a steady stream is a great alternative.
Only use the bone meal powder if your plants require large amounts of calcium or phosphorus. This powder will quickly dissolve in water, providing the nutrients the plants need.
Watch: This Video Can Also Help You
Differences In Prices Between Blood Meal And Bone Meal
Our investigation revealed a pricing range for blood meal from $14 (USD) to $119 (USD). However, the average cost of a bone meal ranges from $9 to $100. As a result, bone meal can save you money if you need to feed your animals.
Watch: You Can Also Look At This Basic Distinction!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the blood meal beneficial to tomatoes?
The tomatoes benefit from the blood meal, you’re right about that. It’s great for fertilizing a wide variety of plants, including tomatoes, thanks to its exceptionally high protein and nitrogen content. Tomato plants benefit from the addition because of the oxygen content of the blood meal, which is roughly 13%. Furthermore, it can help prevent tomato plants from being eaten by critters like moles and deer.
Is it necessary to feed tomato plants with bone meal?
Tomatoes benefit greatly from the usage of bone meal as an organic fertilizer. Phosphorus and nitrogen, two essential plant nutrients, are present. The higher phosphorus content of bone meal causes tomato plants to produce more and larger fruit. Phosphorus encourages robust root growth, while nitrogen promotes luxuriant leaf growth in plants.
Do tomatoes enjoy the taste of blood and bone?
Both blood meal and bone meal are beneficial to tomato plants. This is due to the abundance of essential nutrients, such as phosphorus, calcium, nitrogen, and others, that they provide to tomato plants. Tomato plants do best in soils that are rich in organic matter and natural nutrients. When you combine blood meal and bone meal, you enrich the soil with organic matter and nutrients.
Which is superior, blood meal or bone meal?
Bone meal and blood meal are both excellent alternatives that can help your plants grow stronger and more fruitful. In organic gardening, blood meal is a recommended amendment. Using organic gardening supplies rather as those sourced from animals is the safest alternative. So, if you ask us, the blood supper is the way to go.
Conclude
Ultimately, we can claim that it is difficult to decide between blood meal and bone meal as a fertilizer for tomato plants. Both can be beneficial to your soil, but you should do a test first to establish exactly what your soil needs. The addition of bone meal is among the best ways to replenish soil phosphorus and calcium levels if these elements are deficient.
A lack of nitrogen in the soil can be remedied by adding blood meal. When deciding between blood meal and bone meal for your tomato plants, there are a few other considerations to keep in mind. We hope this information on tomato growth with blood meal and bone meal has been helpful.




